What is a Network Cable and How Does It Work?
In today’s connected world, understanding a network cable is crucial. John Smith, an industry expert, states, “A network cable is the backbone of our digital communication.” It’s essential to know what it is and how it operates.
Network cables facilitate the transfer of data between devices. They connect computers, routers, and switches, making communication seamless. Different types serve various purposes, from home networks to large enterprises. Yet, not all cables are created equal.
Many people overlook the significance of choosing the right network cable. Poor choices can lead to slow speeds and connectivity issues. It’s important to reflect on the needs of your network. Are you using outdated cables? Can your setup be improved? These questions matter in ensuring robust connectivity.

What is a Network Cable?
A network cable is a crucial component in the world of connectivity. It allows devices to communicate within a network. Typically, it consists of copper or fiber optic wires. These wires transmit data signals, enabling everything from internet browsing to video streaming.
When using network cables, it's essential to consider their types. Different cables serve various purposes. For instance, twisted pair cables are common in homes and offices, while fiber optic cables are used for long distances. The choice depends on your needs.
Tips: Ensure you choose the right length for your space. A cable that's too long can lead to unnecessary clutter. Regularly check cables for wear and tear. Damaged cables can disrupt your connection.
Improper installation can lead to issues. Misaligned connectors might cause slow speeds. It's also important to stay informed about advancements in cable technology. Ensure your cables support your internet speed. Avoid using old cables if you're looking for performance.
Types of Network Cables and Their Uses
Network cables are crucial for data transmission. They connect devices and enable communication over local networks. Various types of cables serve specific needs. Understanding these types can enhance network performance.
Twisted pair cables, often used in offices, come in two categories: STP and UTP. STP cables shield against interference, while UTP is more common for everyday applications. According to industry reports, around 80% of networks utilize UTP cables, highlighting their popularity and effectiveness.
Fiber optic cables transmit data at high speeds over long distances. They are increasingly essential in modern infrastructure. As networks expand, fiber optics are a go-to choice. They reduce latency and boost bandwidth.
**Tips:** Always check for compatibility when choosing a cable type. Ensure the length is appropriate for your setup. Avoid excess slack, which can lead to signal loss.
What is a Network Cable and How Does It Work? - Types of Network Cables and Their Uses
| Type of Network Cable | Description | Maximum Length | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethernet Cable (Cat5e) | Standard cable for connecting devices. | 100 meters | Home networks, small offices. |
| Ethernet Cable (Cat6) | Improved performance over Cat5e. | 55 meters at 10 Gbps | Gaming, data centers. |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Transmits data as light signals. | Up to several kilometers | High-speed internet, telecommunications. |
| Coaxial Cable | Used for cable television and internet. | Up to 500 meters | TV, broadband internet services. |
| HDMI Cable | Transmits audio and video signals. | 15 meters (optimal length) | Connecting TVs, projectors, computers. |
How Network Cables Transmit Data
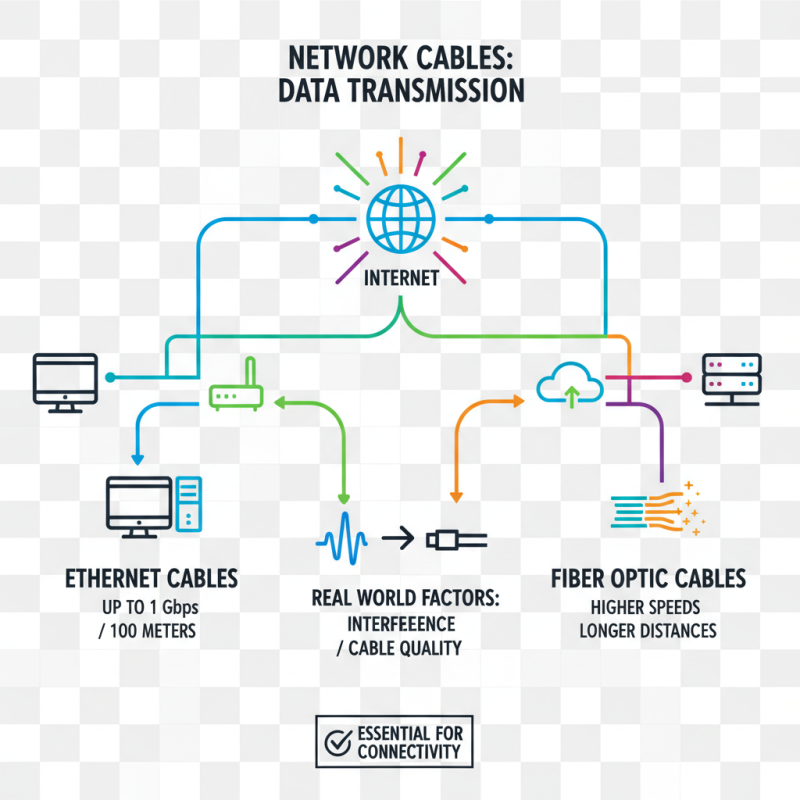
Network cables are essential for data transmission. They connect devices like computers, routers, and switches, facilitating communication over the internet. Various types of cables exist, such as Ethernet and fiber optic. Each type supports different speeds and distances. Ethernet cables, for instance, can transmit data at speeds up to 1 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters. However, in real-world scenarios, factors like interference and cable quality can hinder performance.
Data transmission through network cables occurs via electrical signals or light pulses. In copper cables, electricity relays information in binary code. Each bit transforms into a series of voltage changes. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, use light. These cables can achieve speeds of up to 100 Gbps, making them suitable for high-demand applications. According to industry reports, approximately 80% of global internet traffic is carried through fiber optic networks. Yet, despite these advancements, issues like improper installation and physical damage are frequent challenges.
Recent studies show that network reliability can be impacted by inadequate cabling practices. For example, poor cable management contributes to reduced signal quality. Additionally, using outdated cables can lead to bottlenecks in data flow. It's crucial for businesses to regularly assess their network infrastructures. Upgrading cabling can significantly enhance overall performance. Maintaining optimal connections is as important as selecting the right cable type.
The Construction of a Network Cable
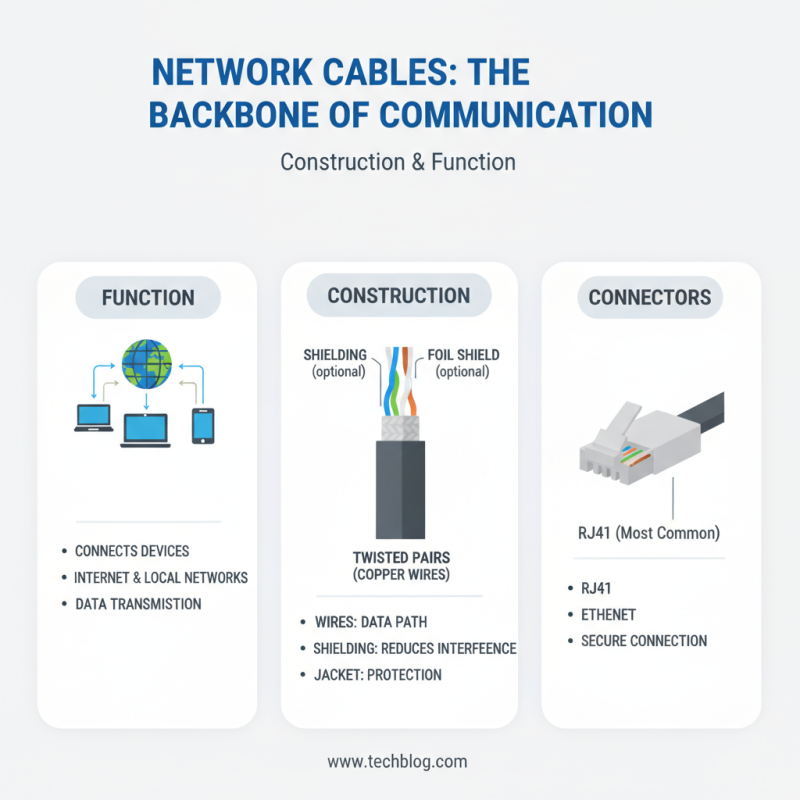
Network cables are essential for communication. They connect devices to the internet and each other. The construction of a network cable is fundamental to its function. A typical network cable consists of wires, shielding, and connectors.
The wires inside are usually twisted pairs. Twisting reduces interference. Each pair is often color-coded to simplify connections. The shielding protects the signal from external noise. The outer layer is robust, designed to withstand wear.
Tips: Check for damage before use. A frayed cable can slow down your network. Keep cables organized to avoid tangles. Too much bending can lead to issues later on. Proper cable management is crucial for maintaining a reliable connection.
Network cables can sometimes be complex. Not all cables perform equally, and using the wrong type can lead to slower speeds. Take your time to understand the options available. Choose wisely to ensure the best network experience possible.
Choosing the Right Network Cable for Your Needs
Choosing the right network cable is crucial for efficient connectivity. With various types available, understanding their differences can save time and enhance performance. Ethernet cables are often a top choice for wired networks. They come in categories like Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a. These categories differ in speed and bandwidth. For instance, Cat6 can support speeds up to 10 Gbps over short distances, making it suitable for high-demand applications.
Tip: Assess your internet usage before selecting a cable. If you stream video in 4K or play online games, opt for at least Cat6. It ensures low latency and high-speed transfers.
Fiber optic cables are another alternative. They transmit data as light, offering greater speed and distance than copper cables. According to industry reports, fiber can achieve speeds exceeding 1 Gbps, which is ideal for businesses with vast data needs. However, fiber installation can be more complex and costly than Ethernet.
Tip: Consider installation logistics when choosing. If budget constraints exist, Ethernet might be more practical. Both cable types have pros and cons, so weigh your options carefully. An informed choice can lead to a more reliable network experience.
Related Posts
-

Understanding Network Cable Types and Their Impact on Internet Speed
-

Top 10 Aerial Cable Benefits You Need to Know for Your Next Project
-

What is Drop Cable and How Does It Work in Telecommunications Industry
-

2025 Top 10 Cable Tube Solutions for Organizing Your Cables Efficiently
-

The Future of Connectivity How Fibre Optic Network Cable is Transforming Communication
-

Transforming Connectivity: The Future of Fibre Optic Infrastructure in Smart Cities
