What is a fibre network and how does it work?
The modern telecommunications landscape is significantly shaped by the development of fibre networks. These networks use optical fibers to transmit data at high speeds. According to a report by Research and Markets, global investments in fibre-optic networks are projected to reach $80 billion by 2027. This robust growth highlights the increasing importance of fibre networks in delivering high-speed internet and multi-gigabit services.
Fibre networks offer unmatched bandwidth and reliability compared to traditional copper lines. They are crucial for supporting cloud computing, streaming services, and remote work. A study from the Fibre Broadband Association indicates that areas with advanced fibre networks experience a 20% increase in economic activity. However, implementing these networks isn't without challenges. The initial costs can be high, and the digging required for installation can disrupt local communities.
Despite these hurdles, the benefits of fibre networks are undeniable. They pave the way for innovations that improve connectivity and efficiency. The transition to fibre networks prompts a reflection on our readiness for such technology. Will we fully embrace its potential? Or will we hold back due to concerns about costs and disruption?

What is a Fibre Network?
A fibre network consists of cables that use light to transmit data. These cables are made from glass or plastic fibers. They are designed to carry signals over long distances with minimal loss. This technology is different from traditional copper lines. Unlike copper, fibre optics are immune to electromagnetic interference. This results in faster and more reliable internet connections.
Fibre networks operate using pulses of light. Data is converted into light signals and sent through the cables. The speed of this transmission is astonishing. Some networks can offer speeds exceeding 1 Gbps. However, not all areas have access to fibre networks. Urban locations typically have better coverage than rural areas. Installing fibre cables can be expensive and complicated. This leads to challenges in service availability.
Maintaining a fibre network also requires ongoing effort. Regular inspections and updates are necessary to ensure efficiency. Some installations may face unexpected issues, like weather damage. Fibre networks are a remarkable advancement, but they are not perfect. They require significant investment and planning. It's a technology that holds great potential for the future, yet requires wise management today.
Components of a Fibre Optic Network
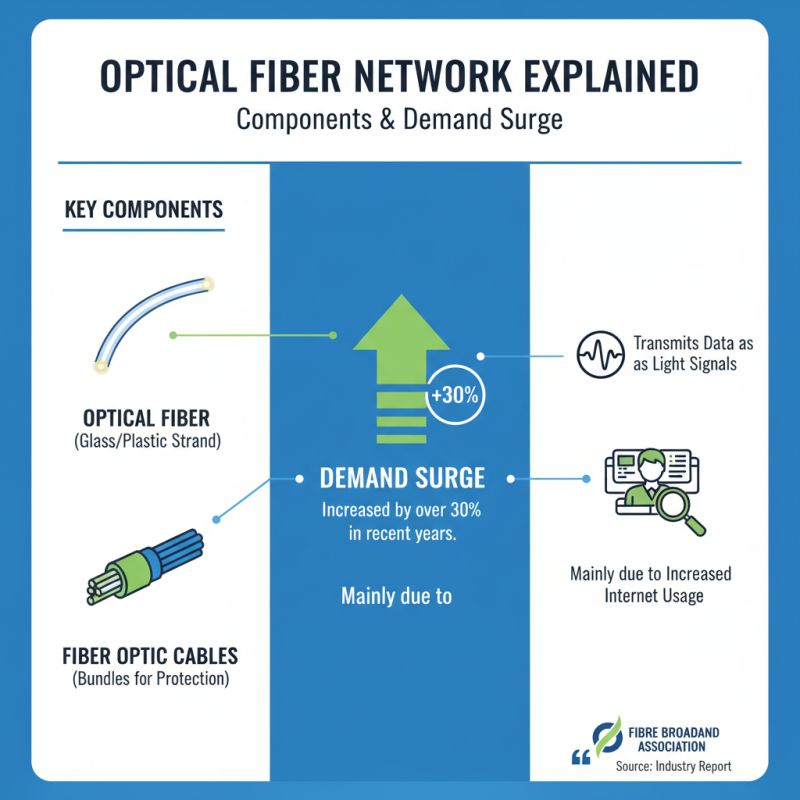
A fibre optic network is composed of several key components. The core element is the optical fibre, a thin strand made of glass or plastic. It transmits data as light signals. These fibres are bundled into cables, protecting them from physical damage and environmental factors. According to a report from the Fibre Broadband Association, the demand for fibre networks has surged by over 30% in recent years, mainly due to increased internet usage.
Another crucial component is the optical transmitter, which converts electrical signals into light signals for transmission. On the receiving end, optical receivers perform the reverse function. These components work seamlessly together. By using fibre optics, networks achieve higher speeds and greater bandwidth compared to traditional copper cables. Research from the International Telecommunication Union indicates that fibre networks can support data speeds exceeding 1 Gbps.
Tips: Ensure proper installation to maximize network efficiency. Regular maintenance can help identify potential issues early. Layering protections against physical stress is vital. Plan your layout carefully to avoid unnecessary complications down the line. Mistakes in this stage can lead to significant downtime and costly repairs.
How Fibre Networks Transmit Data
Fibre networks are a modern marvel, designed to transmit data at astonishing speeds. They use light to send information through thin strands of glass or plastic. This technology allows for faster downloads, smoother streaming, and seamless communication.
When data travels through a fibre network, it gets converted into light signals. These signals move at incredible speeds, much faster than traditional copper wires. The light bounces along the cable, allowing it to travel long distances without losing quality. This efficiency is a game changer for businesses and homes alike.
However, fibre networks are not without challenges. Installation can be complex and costly. Not all areas have access to this technology yet. Additionally, while fibre offers speed, the infrastructure must be maintained to ensure reliability. Overcoming these challenges will take time and investment but can revolutionize the way we connect and communicate.
Advantages of Using Fibre Optic Technology
Fibre optic technology offers significant advantages that make it a preferred choice for data transmission. One of its main benefits is speed. Fibre networks can transmit data at incredible speeds, often reaching gigabits per second. This efficiency is ideal for activities like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing. Users can enjoy a seamless experience without interruptions.
Another key advantage is bandwidth capacity. Fibre optics can handle a massive amount of data simultaneously. This makes it suitable for both residential and commercial purposes. In densely populated areas, a fibre network can accommodate numerous users without slowing down. However, deploying a fibre network can be expensive and time-consuming, which raises concerns for some organizations.
Fibre networks also offer improved reliability. They are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference, ensuring stable connections. This reliability is crucial for businesses that depend on constant data flow. Yet, it's worth noting that fibre installation requires skilled professionals. Mistakes during installation can lead to performance issues. Balancing these advantages with the challenges is essential for informed decisions.
Common Applications of Fibre Networks
Fibre networks are becoming increasingly popular. They provide fast and reliable internet connections globally. These networks use thin strands of glass or plastic signals to transmit data as light. This technology supports various applications that enhance everyday activities.
One common application of fibre networks is in residential internet services. Home users enjoy high-speed internet for streaming, gaming, and video calls. Schools also benefit from fibre networks. They enable smooth online learning experiences, allowing students to access educational materials quickly.
Businesses leverage fibre networks for communication and collaboration. High-speed connections support cloud services, data storage, and online meetings. However, not every location has access to fibre. Some areas still rely on older technologies. This disparity raises questions about the digital divide. Efficiently bridging this gap remains a crucial challenge.
What is a Fibre Network and How Does it Work? - Common Applications of Fibre Networks
| Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Broadband Internet | High-speed internet access using fiber optic cables. | Fast speeds, reliable connections, and higher bandwidth. |
| Telecommunications | Transmission of voice and data over long distances. | Reduced latency and enhanced call quality. |
| Video Streaming | Delivering high-definition video content online. | Improved buffering and superior picture quality. |
| Cloud Services | Accessing cloud-based applications and storage. | Faster data transfers and enhanced security. |
| Smart Cities | Integration of digital technologies in urban infrastructure. | Improved efficiency and enhanced citizen services. |
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future of Connectivity: How Fibre Networks are Revolutionizing Internet Access
-

What are the Best Practices for Generating Fibre Leads?
-

2026 Top Trends in Underground Fibre Optic Cable Technology?
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Fibre Network for Your Home
-

Exploring the Benefits of Underground Ducting for Fibre Optic Cable Installation
-

Exploring the Future of Connectivity with Aerial Fibre Cable Technology
