What is Fibre Cable and How Does It Work for Your Connectivity Needs
Fibre cable technology has transformed the landscape of connectivity, offering unparalleled speed and reliability that is critical in today’s fast-paced digital world. As John Smith, a renowned expert in the field of telecommunications, aptly stated, “Fibre cables are the backbone of modern communication, enabling rapid data transfer that meets the demands of everything from streaming services to cloud computing.” This article aims to demystify what fibre cables are and how they function to fulfill a variety of connectivity needs.
In an age where high-speed internet access is imperative for both personal and professional use, understanding the mechanics behind fibre cable technology is crucial. Unlike traditional copper cables, fibre cables utilize light to transmit data, which significantly enhances their capacity and performance. This introduction will explore the fundamental principles of fibre cable technology, its advantages over conventional connections, and the role it plays in supporting an increasingly interconnected world. As we dive into the intricacies of fibre cables, it becomes evident that they are not just a technological marvel but a necessary infrastructure for sustaining modern communication systems.
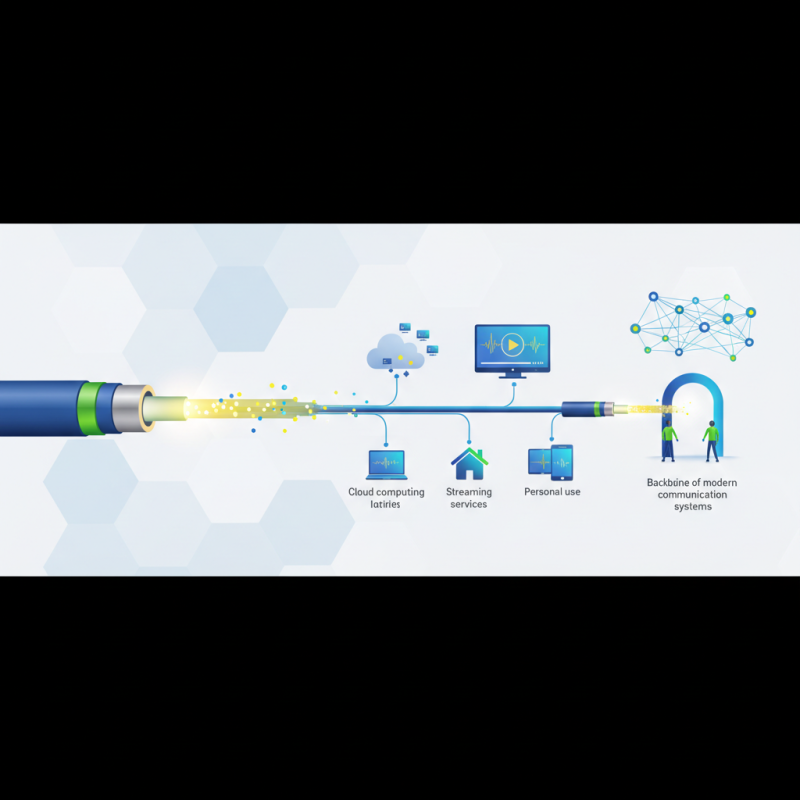
What is Fibre Cable: Definition and Overview
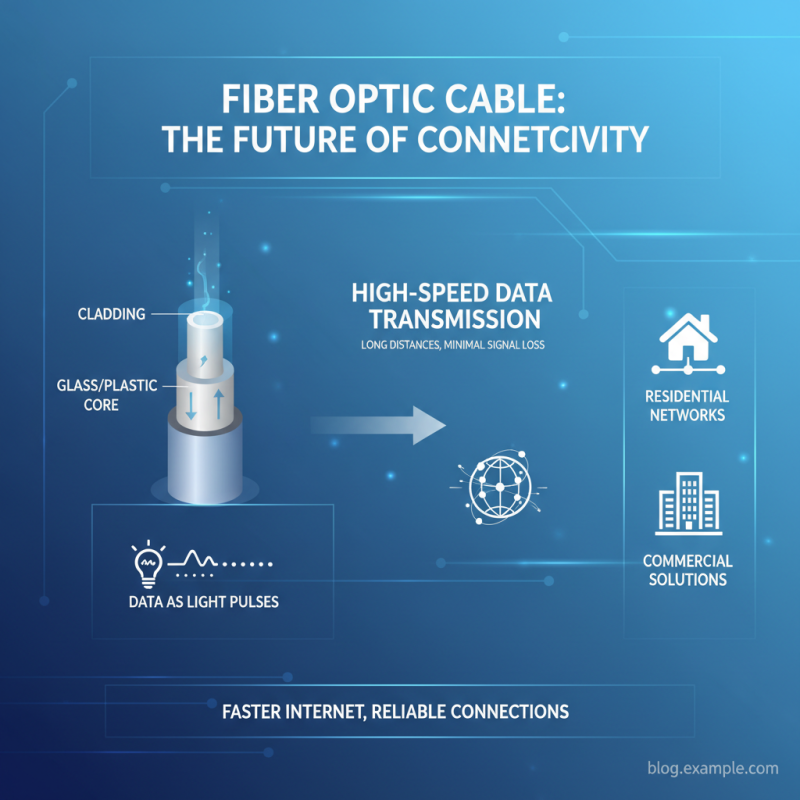
Fibre cable, also known as optical fibre, is a technology that uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. This method of data transmission allows for high-speed communication over long distances with minimal signal loss. The core of the fibre is surrounded by a cladding material that reflects light back into the core, enabling the signal to travel effectively. As demand for faster internet and more reliable connections continues to grow, fibre cable has emerged as a crucial component in both residential and commercial networking solutions.
When considering fibre cable for your connectivity needs, it’s essential to understand its advantages. Fibre cables offer significantly higher bandwidth compared to traditional copper cables, making them ideal for environments that require heavy data usage, such as data centers and large enterprises. Additionally, fibre cables are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference, leading to improved performance in various settings.
**Tips for Choosing Fibre Cable:**
1. Assess your bandwidth requirements: Determine the speed and amount of data you need to transmit to select the appropriate fibre type.
2. Consider installation costs: While fibre cables may have higher upfront costs, their long-term benefits in speed and reliability can lead to overall savings.
3. Evaluate your environment: The physical conditions of your installation site can impact performance; ensure you choose a fibre type that meets your specific environmental needs.
Types of Fibre Cables: Single Mode vs. Multi-Mode
Fibre cables are a crucial component in modern communication networks, particularly due to their ability to transmit data at high speeds over long distances. When it comes to fibre cables, there are two primary types: Single Mode and Multi-Mode. Single Mode fibre optics have a small core diameter—typically around 8 to 10 microns—which allows only one mode of light to propagate. This feature makes them ideal for long-distance communication, supporting distances up to 80 km or more without significant signal loss. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union, Single Mode installations are becoming increasingly prevalent in backbone links and metropolitan area networks due to their efficient performance.
On the other hand, Multi-Mode fibre cables have a larger core diameter, generally ranging from 50 to 62.5 microns, allowing multiple light modes to transmit simultaneously. This design makes them suitable for shorter distances, typically under 2 km. Multi-Mode fibres are often used in local area networks (LANs) and data centers, as they balance performance with cost-effectiveness. Market research from Optica indicates that Multi-Mode fibre’s share in the fibre optic cable market remains significant, particularly in environments where high bandwidth is needed over shorter distances.
Tips: When evaluating fibre cable options, consider the distances you will be covering and the bandwidth requirements of your applications. If you anticipate needing to expand your network in the future, investing in Single Mode fibre could provide better long-term value. For installations such as office buildings or campuses, Multi-Mode fibre may offer a more cost-efficient solution without sacrificing performance for the required ranges.
How Fibre Optic Technology Works: The Science Behind Connectivity
Fibre optic technology has revolutionized how we achieve connectivity by utilizing the principles of light transmission to send data. At the core of this technology are thin glass or plastic fibers, which transmit light signals over long distances with minimal loss. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), fibre optic networks can offer data speeds of 1 Gbps and beyond, significantly outpacing traditional copper lines that average around 100 Mbps. The use of light pulses to convey information allows fibre optics to carry vast amounts of data simultaneously, making it particularly valuable for internet service providers and telecommunications.
The science behind fibre optics lies in the phenomenon of total internal reflection. When light travels through a medium such as glass, it can reflect off the walls of the fiber if it meets the interface at a specific angle, known as the critical angle. This enables the light to be contained within the fiber, preventing signal degradation over distances that can extend up to several kilometers. According to research from the Fiber Broadband Association, the deployment of fibre optic infrastructure is projected to enable connectivity to over 80% of U.S. households by 2025, underscoring its importance in the global push for high-speed internet access and the growth of smart cities. The efficiency and reliability of fibre optics position it as the backbone of modern communication networks, paving the way for advancements in the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and beyond.
Fibre Optic Cable Bandwidth Comparison
This chart illustrates the bandwidth capabilities of various types of cables commonly used for connectivity. Single-mode fiber offers the highest bandwidth, making it suitable for long-distance communication, while multi-mode fiber has lower capabilities, and traditional copper cables like Cat5e and Cat6 are much more limited.
Benefits of Fibre Cables for Modern Communication Needs
Fibre cables have emerged as a crucial technology for modern communication, offering numerous benefits that significantly enhance connectivity. One of the primary advantages of fibre optic cables is their ability to transmit data at incredibly high speeds. Unlike traditional copper cables, which struggle with signal degradation over long distances, fibre cables maintain their performance, allowing for uninterrupted data flow. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high bandwidth, such as streaming, online gaming, and large data transfers.
Moreover, fibre cables are renowned for their resistance to electromagnetic interference, providing a more stable and reliable connection. This characteristic is especially important in environments where electronic devices might disrupt signals. Additionally, fibre optics are more secure as they are harder to tap into compared to copper cables, offering a degree of protection against potential data breaches. As businesses and homes increasingly demand faster and more reliable internet connections, the advantages of fibre cables make them an indispensable asset in fulfilling modern communication needs.
Applications of Fibre Cable in Various Industries and Settings
Fibre cable has become a crucial component in various industries, providing high-speed data transmission capabilities essential for modern communications. In the telecommunications sector, fibre optic cables are utilized to support internet services, telephone networks, and cable television. Their ability to transmit data over long distances at incredibly high speeds makes them an ideal choice for urban infrastructures and rural connectivity solutions, significantly enhancing the quality and reliability of communication services.
Beyond telecommunications, the healthcare industry has also embraced fibre cable technology. Hospitals and medical facilities use fibre optics for data transmission in imaging systems, allowing for faster sharing of diagnostic information. Furthermore, fibre optics are found in surgical environments, where they enable high-resolution imaging that assists in minimally invasive procedures. The manufacturing sector relies on fibre optic sensors for monitoring production lines, ensuring quality control and enhancing safety measures. With these diverse applications, fibre cable continues to revolutionize the way industries operate, supporting the growing demand for efficient, high-speed connectivity.
Related Posts
-

2025 Guide: How to Optimize Your Fibre Cable Installation for Maximum Efficiency
-

What is Fibre Drop Cable and Its Uses in Network Installation
-

2025 Top 10 Cable Tube Solutions for Organizing Your Cables Efficiently
-

Understanding Network Cable Types and Their Impact on Internet Speed
-

Exploring the Benefits of Underground Ducting for Fibre Optic Cable Installation
-

2025 Top Fibre Optic Installation Trends for Enhanced Connectivity Solutions
