10 Essential Tips for Building Effective Fibre Optic Infrastructure?
Fibre optic infrastructure is the backbone of modern communication networks. In recent years, the global demand for high-speed internet has skyrocketed, emphasizing the need for robust fibre optic solutions. According to a report by the Global Market Insights, the fibre optic cable market is projected to reach $15 billion by 2026, driven by increasing data traffic and the growth of smart technologies.
Building effective fibre optic infrastructure is not without challenges. Issues like installation costs, environmental considerations, and regulatory hurdles can hinder progress. Yet, the benefits are undeniable. Faster data transmission and improved reliability can transform businesses and enhance connectivity. A careful approach is essential for success, focusing on quality materials and strategic planning.
Moreover, it’s important to reflect on past projects. Some have faced delays and budget overruns. Learning from these experiences can lead to better decision-making. For companies looking to expand their fibre optic networks, understanding these complexities is crucial. Embracing best practices can ensure that investments yield the expected returns.

Identifying Key Requirements for Fibre Optic Infrastructure Development
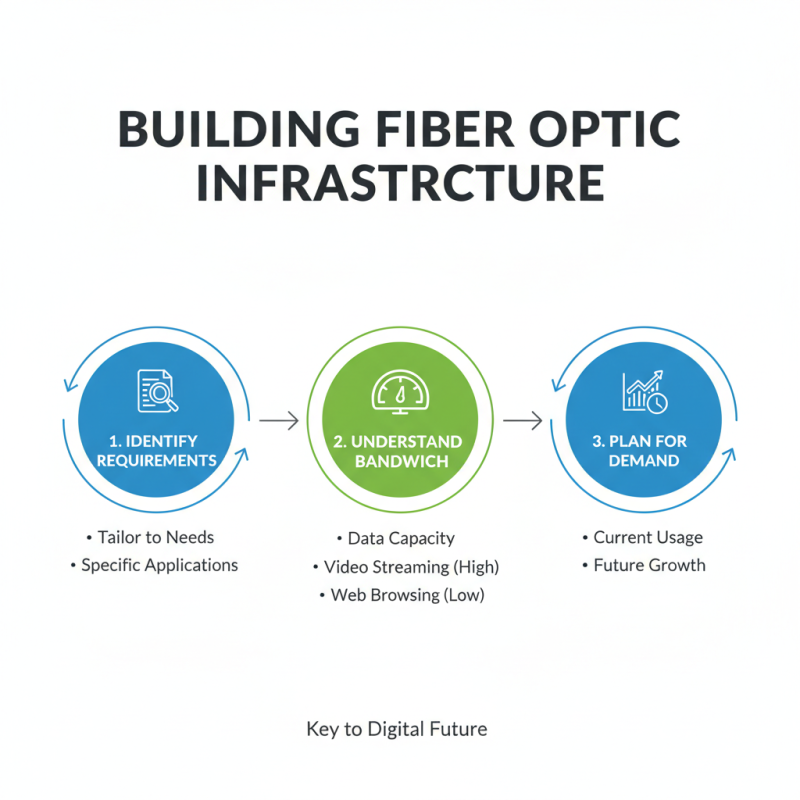
Building effective fibre optic infrastructure begins with identifying key requirements tailored to specific needs. Understanding the bandwidth requirements is crucial. Different applications may demand varying levels of data capacity. For instance, video streaming services need more bandwidth than basic web browsing. Assessing current and future demands helps in planning.
Another significant factor is the geographical layout. Urban areas might require denser cabling networks compared to rural regions. Consideration of environmental factors is also vital. Extreme weather conditions can impact infrastructure durability. Neglecting these aspects may lead to costly repairs later.
Furthermore, involve key stakeholders in the planning phase. Their insights can provide valuable context. Collaborate with local utilities, planning authorities, and communities. Miscommunication can result in infrastructure that fails to meet user needs. Keeping open channels for feedback is essential for ongoing improvements.
Choosing the Right Materials and Equipment for Fibre Optic Networks
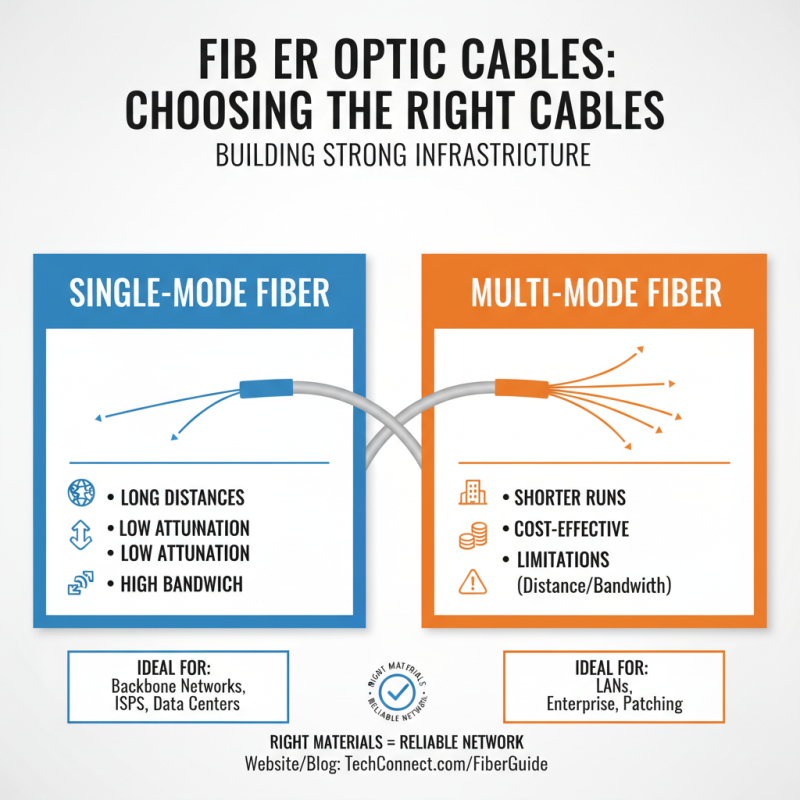
Building a strong fibre optic infrastructure starts with choosing the right materials and equipment. The right cables matter deeply. Single-mode fibres are great for long distances. They offer low attenuation and high bandwidth. Multi-mode fibres work well for shorter runs. They can be more cost-effective, but they come with limitations.
When selecting equipment, focus on connectors and splicing methods. Quality connectors ensure minimal signal loss. Ensure they match your fibre type. Poorly chosen connectors can cause headaches down the road. Splicing methods also impact performance. Fusion splicing offers lower loss than mechanical splicing, but it may be more complex.
Pay attention to installation conditions. Environmental factors can affect performance. For example, extreme temperatures may impact materials. Always use protective conduits. They guard against physical damage and moisture. Plan for the future. Technology evolves, and you may need upgrades. Space for additional fibres can save time later. Building fibre optic infrastructure is an ongoing journey. Reflect on your choices to ensure lasting success.
Understanding Installation Best Practices for Fibre Optic Cables
When considering fibre optic installation, several best practices should be emphasized for success. Proper handling of the cables is critical. Fibre optic cables are delicate. A small bend can cause significant damage. According to industry reports, almost 30% of installation errors stem from improper bending. It’s vital to adhere to the minimum bend radius specified by manufacturers. This minimization of stress on cables can prevent future issues.
Environmental factors also play a significant role. Cables should be protected from extreme temperatures. For example, temperatures below -20°C can impair signal quality. Regularly checking the installation site for moisture is essential. Moisture can lead to fibre degradation over time. Reports indicate that nearly 25% of fibre failures are linked to environmental factors.
Lastly, skilled labor is a non-negotiable requirement. Training installers ensure they understand the intricacies of the materials. It’s said that poorly trained technicians increase the likelihood of installation mistakes by 40%. Continuous education in industry standards is beneficial. Investing in skilled labor pays off in reliability and performance. Reflecting on these practices helps in recognizing areas for improvement during installations.
Fiber Optic Installation Best Practices
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
When building fibre optic infrastructure, compliance with industry standards is crucial. According to a recent report by the International Telecommunication Union, non-compliance can lead to costly delays and fines. Therefore, ensuring adherence to relevant regulations is vital for project success.
One essential tip is to familiarize your team with local and international standards. The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) outlines these norms, which include installation practices and safety measures. Knowledge of standards helps in avoiding pitfalls.
Implementing regular audits is another effective strategy. These audits ensure your infrastructure meets all compliance requirements. A study by the Fiber Optic Association found that projects with consistent oversight had a 30% higher success rate. This emphasizes the importance of accountability.
Consulting with industry experts can provide valuable insights. Their experience helps identify potential compliance issues early. More often than not, overlooked details can lead to major setbacks in project timelines. Recognizing this can promote a proactive approach to fibre optic infrastructure development.
10 Essential Tips for Building Effective Fibre Optic Infrastructure
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Key Considerations | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conduct a Site Survey | Assess environmental factors and existing infrastructure. | OSHA, NEC |
| 2 | Choose the Right Cable Type | Select between single-mode and multi-mode cables based on usage. | ANSI/TIA |
| 3 | Plan for Future Expansion | Incorporate flexibility in infrastructure design. | IEEE |
| 4 | Ensure Proper Installation Techniques | Follow best practices to avoid damage to fibers. | ISO/IEC |
| 5 | Use Quality Connector and Splice Techniques | Ensure low loss and optimal performance. | TIA/EIA |
| 6 | Conduct Regular Maintenance | Schedule routine checks for degradation signs. | NTT, ISO |
| 7 | Implement Robust Testing Procedures | Verify performance and identify issues promptly. | TIA-568 |
| 8 | Document Everything | Keep detailed records of installations and modifications. | RICS, PMI |
| 9 | Train Your Personnel | Provide ongoing education on current standards. | BICSI, ANSI |
| 10 | Stay Informed on Industry Changes | Monitor updates to laws and regulations. | FCC, NIST |
Implementing Effective Maintenance Strategies for Long-Term Performance
Effective maintenance strategies are crucial for the longevity of fibre optic infrastructure. Regular inspections can uncover issues before they escalate. For instance, a recent report indicated that preventative maintenance can reduce downtime by up to 40%. This involves routine checks and timely repairs. Regular documentation helps track performance over time and identifies recurring issues.
Moreover, environmental factors can affect the infrastructure significantly. Moisture, temperature, and physical stress impact fibre optic cables. A proactive approach to maintenance must consider these factors. Research shows that about 30% of fibre failures are due to environmental conditions yet remain unaddressed in many installations. Implementing humidity and temperature monitoring systems can enhance performance.
Training teams is essential, too. A skilled workforce can implement best practices during maintenance. However, many organizations still underestimate the value of continuous training. Data suggests that incidents caused by human error could rise by 20% without proper education. Reflecting on these challenges will lead to better future performance.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Fibre Optic Internet Service
-

Transforming Connectivity: The Future of Fibre Optic Infrastructure in Smart Cities
-

The Future of Connectivity How Fibre Optic Network Cable is Transforming Communication
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Fibre Network for Your Home
-

2025 Guide: How to Optimize Your Fibre Cable Installation for Maximum Efficiency
-

10 Essential Tips for Building Efficient Fibre Optic Infrastructure
